|
Introduction: Orthodontics is a field that continuously evolves, seeking to provide patients with not only a beautiful smile but also improved overall health and well-being. Orofacial myology, a specialized branch of therapy, can play a pivotal role in helping orthodontists achieve the best results for their clients.
Understanding Orofacial Myology: Orofacial myology, also known as myofunctional therapy, is a holistic approach that focuses on the muscles of the face, mouth, and throat. These muscles play a significant role in various functions, including breathing, swallowing, and speaking. When the orofacial muscles function optimally, it promotes proper craniofacial development, reduces the risk of orthodontic issues, and supports overall health. How Orofacial Myology Benefits Orthodontic Treatment:
Collaboration between Orthodontists and Orofacial Myologists: To fully realize the benefits of myofunctional therapy, orthodontists can collaborate with orofacial myologists. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that orthodontic treatment is customized to address not only the alignment of teeth but also the underlying muscle functions. Conclusion: Orofacial myology plays a vital role in optimizing orthodontic outcomes for clients. By addressing the function of orofacial muscles, orthodontists can achieve more efficient treatment, reduce relapse, and enhance overall patient well-being. Embracing myofunctional therapy as an integral part of orthodontic care ensures that patients not only leave with a beautiful smile but also with improved health and quality of life.
0 Comments
Introduction: Sleep is an essential aspect of a child's development, promoting physical growth, cognitive function, and emotional well-being. As a myofunctional therapist, I have observed the intricate link between sleep quality and a child's behavior. In this post, we will explore the significant impact that poor quality sleep can have on a child's behavior, highlighting the importance of addressing sleep-related issues to support their overall health and development. Disrupted Sleep Cycles and Emotional Regulation: When a child's sleep is consistently disrupted or of poor quality, it can lead to imbalances in their sleep cycles. Insufficient or fragmented sleep impairs the child's ability to regulate emotions effectively, resulting in mood swings, irritability, increased emotional sensitivity, and difficulty managing stress. Adequate, restful sleep supports emotional resilience and helps children navigate their daily experiences with greater ease. Cognitive Functioning and Attention Difficulties: Sleep deprivation or poor quality sleep significantly impacts a child's cognitive functioning. Insufficient sleep can lead to difficulties with concentration, memory, and attention span. These cognitive challenges can manifest as decreased academic performance, reduced ability to focus and learn, and an overall decline in cognitive abilities. By ensuring quality sleep, we optimize a child's cognitive abilities and set the stage for successful learning and development. Hyperactivity and Impulsivity: Sleep deprivation has been linked to increased hyperactivity and impulsivity in children. When a child is tired, they may exhibit excessive fidgeting, restlessness, and difficulty sitting still. Lack of quality sleep can exacerbate symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and contribute to behavioral challenges, making it harder for a child to self-regulate and engage in appropriate social interactions. Behavioral Issues and Emotional Dysregulation: Poor quality sleep can lead to a range of behavioral issues. Sleep-deprived children may display increased aggression, defiance, and oppositional behaviors. They may struggle to follow rules, have difficulty coping with frustration, and display impulsiveness in their actions. By addressing sleep-related concerns, we can help children develop healthier behavioral patterns, fostering positive interactions with others and improving their overall quality of life. Growth and Developmental Delays: Adequate sleep is crucial for a child's growth and development. During sleep, the body releases growth hormones that support physical development. Lack of quality sleep can hinder proper growth, leading to potential delays in height, weight, and overall development. By prioritizing healthy sleep habits, we provide children with the necessary conditions for optimal growth and development. Myofunctional Therapy and Sleep-Related Issues: Myofunctional therapy plays a significant role in addressing sleep-related issues. By focusing on optimizing oral function, myofunctional therapists help correct oral habits that can impact sleep quality, such as mouth breathing, incorrect tongue posture, and muscular imbalances. Myofunctional therapy supports nasal breathing, proper tongue positioning, and overall muscle balance, facilitating better airflow, improved sleep quality, and ultimately enhancing a child's behavior and well-being. Conclusion: The connection between poor quality sleep and a child's behavior is undeniable. Sleep deprivation and fragmented sleep can significantly impact a child's emotional regulation, cognitive abilities, attention span, and behavior. As myofunctional therapists, we recognize the critical role that sleep plays in a child's overall health and development. By addressing sleep-related issues through proper sleep hygiene, identifying and treating oral function concerns, and promoting healthy sleep habits, we can support children in achieving restful, rejuvenating sleep and fostering positive behavior, emotional well-being, and optimal growth and development. Introduction: Breathing is a fundamental process that sustains our lives, but did you know that the way we breathe can profoundly impact our health and well-being? As a myofunctional therapist, I am passionate about educating individuals on the importance of nasal breathing. In this post, we will explore the remarkable benefits of nasal breathing and why it plays a pivotal role in optimizing oral function, overall health, and well-being.
The Physiology of Nasal Breathing: Nasal breathing involves inhaling and exhaling through the nose rather than the mouth. Our nasal passages are equipped with a complex system designed to filter, humidify, and warm the incoming air. The nose also produces nitric oxide, a gas that has antimicrobial properties and supports various physiological functions within the body. Improved Oxygenation and Energy Levels: Nasal breathing allows for efficient oxygen exchange in the lungs. The nasal passages and sinuses act as natural filters, capturing airborne particles and allergens, thereby preventing them from reaching the lower airways. This filtration process helps reduce respiratory infections and allergies, ultimately promoting better oxygenation and increased energy levels. Optimal Airway Function and Respiratory Health: The intricate nasal anatomy and the turbinates within the nasal cavity help regulate airflow and optimize airway function. Nasal breathing promotes proper lung ventilation, enhances lung capacity, and supports respiratory health. It also aids in regulating breathing patterns, preventing hyperventilation, and promoting a balanced exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Humidification and Protection: Nasal breathing ensures that the air we inhale is adequately humidified, preventing dryness and irritation of the airways. The nasal passages' mucus layer traps bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, preventing them from entering the respiratory system. This crucial defense mechanism helps protect against respiratory infections and promotes a healthy respiratory environment. Oral Health and Facial Development: The act of nasal breathing influences oral health and facial development. When we breathe through the nose, the tongue rests against the palate, exerting gentle pressure that aids in proper dental arch development and alignment. Nasal breathing also supports optimal muscle tone in the orofacial region, preventing issues such as open-mouth posture, dental malocclusion, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. Improved Sleep and Overall Well-being: Nasal breathing is closely tied to quality sleep. Breathing through the nose promotes relaxation, reduces snoring, and helps prevent sleep-disordered breathing conditions such as obstructive sleep apnea. Sound sleep, in turn, contributes to better cognitive function, mood regulation, and overall physical and mental well-being. Myofunctional Therapy and Nasal Breathing: Myofunctional therapy plays a vital role in promoting and restoring nasal breathing. By addressing orofacial muscle imbalances, tongue posture, and swallowing patterns, myofunctional therapy helps individuals transition from mouth breathing to nasal breathing. Therapists guide patients through exercises that strengthen the muscles involved in breathing, swallowing, and tongue function, facilitating the shift to healthy nasal breathing habits. Conclusion: Nasal breathing is not just a basic physiological process; it is a gateway to improved health, well-being, and optimal oral function. Embracing nasal breathing can enhance oxygenation, support respiratory health, protect against infections, aid in oral and facial development, improve sleep quality, and positively impact overall well-being. As a myofunctional therapist, I emphasize the importance of nasal breathing and work with individuals to optimize their breathing patterns, helping them unlock the incredible benefits that nasal breathing offers. Introduction: Sucking habits are common in infancy, but when they persist beyond the appropriate age, they can have significant consequences for oral health and development. As a myofunctional therapist, I have witnessed the profound impact of sucking habits on individuals of all ages. In this post, we will explore the consequences of prolonged sucking habits and shed light on the transformative role that myofunctional therapy plays in breaking free from these habits and promoting optimal oral health. The Impact of Prolonged Sucking Habits: Prolonged thumb or finger sucking, pacifier use, or other non-nutritive sucking habits can exert mechanical forces on the oral structures, leading to malocclusion (misalignment of teeth) and improper jaw development. The pressure from sucking habits can disrupt the balance of forces in the oral cavity, affecting the position of the tongue, the growth of the jaws, and the alignment of the teeth. Malocclusion and Dental Issues: Sucking habits can contribute to various dental issues, such as open bite (gap between the upper and lower teeth when biting), crossbite (misalignment of the upper and lower jaws), and protrusion of the front teeth. These malocclusions can not only affect the aesthetics of the smile but also impact chewing efficiency, speech clarity, and overall oral function. Tongue Posture and Muscular Imbalances: Prolonged sucking habits can influence tongue posture and function. The constant presence of a pacifier or thumb in the mouth can displace the tongue from its natural resting position against the palate. This disruption in tongue posture can lead to orofacial muscle imbalances, including tongue thrust swallowing patterns, further exacerbating the impact on dental and facial development. Speech and Language Challenges: Sucking habits can also interfere with speech and language development. Improper tongue positioning and muscle imbalances caused by sucking habits can affect articulation, making it difficult to pronounce certain sounds or form words correctly. This can impact a child's ability to communicate effectively and may require speech therapy interventions. Myofunctional Therapy for Breaking Sucking Habits: Myofunctional therapy is a specialized approach that addresses the underlying causes of sucking habits and provides effective strategies for breaking free from these habits. Through exercises, techniques, and behavioral modifications, myofunctional therapists help individuals retrain oral muscles, promote proper tongue posture, and establish healthy swallowing patterns. Restoring Oral Function and Promoting Dental Health: Myofunctional therapy goes beyond breaking sucking habits; it also focuses on restoring optimal oral function and promoting dental health. By addressing muscle imbalances, improving tongue posture, and facilitating proper chewing and swallowing, myofunctional therapy helps realign the teeth and jaws, enhancing oral health and overall well-being. Early Intervention and Long-Term Benefits: Early intervention is crucial in addressing sucking habits and preventing long-term consequences. The sooner an individual receives myofunctional therapy, the better the chances of correcting oral issues and minimizing the need for more invasive treatments, such as orthodontics, in the future. Myofunctional therapy offers long-term benefits by promoting healthy oral habits and laying the foundation for optimal growth and development. Conclusion: Sucking habits can have far-reaching implications for oral health, speech development, and overall well-being. However, myofunctional therapy offers a positive, transformative solution by addressing the underlying causes, breaking the habit, and promoting optimal oral function. By seeking early intervention and working with a myofunctional therapist, individuals can overcome sucking habits, achieve proper oral alignment, and unlock a lifetime of improved oral health and confident smiles. Tongue Ties and Their Impact on Growth and Development: The Vital Role of Myofunctional Therapy6/16/2023 Introduction: Tongue ties, formally known as ankyloglossia, are a condition that affects the tongue's ability to move freely due to an unusually tight or short frenulum. While often considered a minor issue, tongue ties can have significant implications for growth and development, particularly in children. In this post, we will explore how tongue ties can impact various aspects of an individual's well-being and highlight the crucial role that myofunctional therapy plays in optimizing outcomes following a tongue tie release.
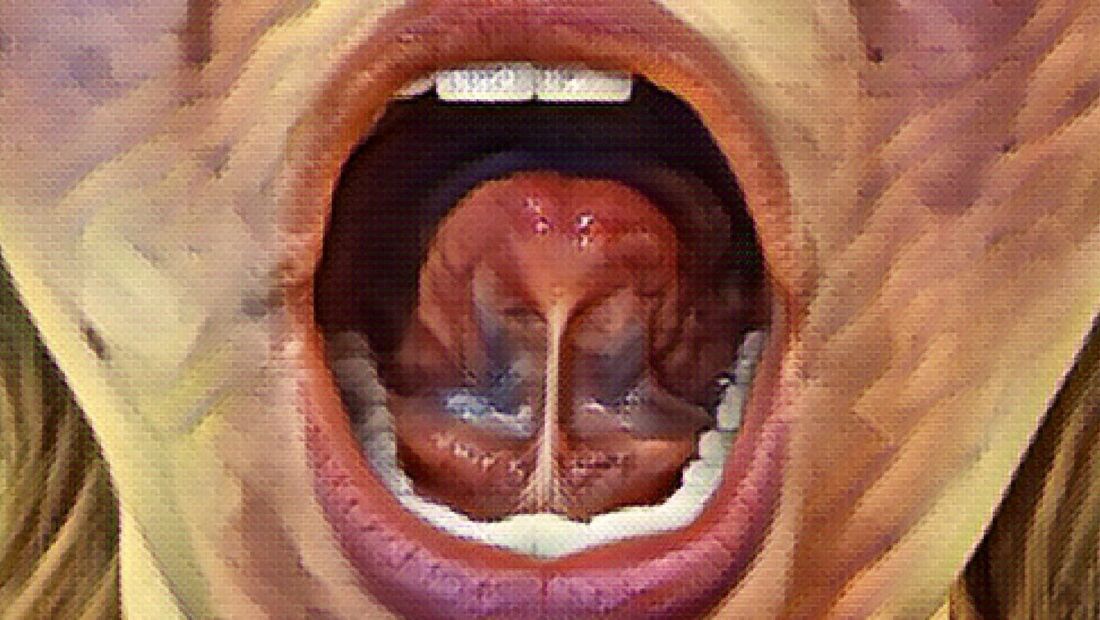
The Role of the Tongue in Oral Function: The tongue serves several vital functions, including speech, swallowing, breathing, and oral posture. When a tongue tie restricts the tongue's range of motion, it can disrupt these functions, leading to potential complications and developmental challenges. Impaired Breastfeeding and Early Feeding Difficulties: Tongue ties can significantly affect newborns' ability to breastfeed effectively. Infants with tongue ties may struggle to latch onto the breast, leading to inadequate milk transfer, poor weight gain, and frustration for both the baby and mother. Early identification and intervention can support successful breastfeeding and improve feeding efficiency. Speech and Articulation Issues: As children grow, an unreleased tongue tie can contribute to speech and articulation difficulties. The tongue's restricted mobility may hinder proper formation of sounds, resulting in lisps, difficulty pronouncing certain letters, or other speech disorders. Myofunctional therapy, post-release, helps retrain the tongue's movement patterns and supports the development of clear and accurate speech. Orofacial Growth and Dental Alignment: Tongue ties can influence the development of the orofacial structures, including the jaw, palate, and teeth. The continuous pressure exerted by a tethered tongue can alter the natural growth trajectory of these structures, leading to issues such as narrow dental arches, malocclusion (misalignment of teeth), and other orthodontic problems. Myofunctional therapy plays a critical role in correcting these issues by promoting proper tongue posture, encouraging nasal breathing, and facilitating harmonious orofacial growth. Breathing and Sleep Disorders: A tongue tie can affect the airway and breathing patterns. When the tongue is unable to rest in the correct position against the palate, mouth breathing may become the norm, potentially leading to sleep-disordered breathing conditions like snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. Myofunctional therapy aims to establish nasal breathing and proper tongue posture, helping to improve airway function and promote restful sleep. Long-term Effects on Overall Health: Unaddressed tongue ties can have far-reaching consequences for an individual's overall health and well-being. Chronic oral and facial muscle tension, poor digestion, and even postural issues may arise due to the compensatory behaviors associated with a restricted tongue. By undergoing myofunctional therapy post-release, individuals can restore proper muscle function and mitigate potential long-term health complications. Conclusion: Tongue ties can significantly impact growth and development across various domains, including breastfeeding, speech, dental alignment, breathing, and overall health. Recognizing the importance of myofunctional therapy as an integral part of the treatment process following tongue tie release is crucial. By working with a myofunctional therapist, individuals can optimize their oral function, promote healthy growth and development, and enhance their overall quality of life. Introduction: Tongue tie, or ankyloglossia, is a condition characterized by a shortened lingual frenum, which restricts the movement of the tongue. Often overlooked and undiagnosed, tongue tie can have significant consequences on a person's growth, development, and overall health. As a dental hygienist with expertise in orofacial myology, I have witnessed the profound effects of untreated tongue ties and the benefits of intervention. In this blog post, we will delve into the multifaceted impact of tongue tie, ranging from breastfeeding difficulties in infancy to speech challenges, sleep disruptions, and associated issues throughout life. We will also explore the role of myofunctional therapy in addressing tongue tie and promoting optimal health and well-being. Difficulty Nursing as an Infant: Tongue tie can be a significant hurdle when it comes to successful breastfeeding. The limited mobility caused by a tongue tie can exhaust the infant while nursing, leading to inadequate milk intake. This not only affects the baby's growth but can also impact the mother's milk supply and increase the risk of issues such as mastitis. Proper assessment and treatment of tongue tie can help alleviate breastfeeding challenges and promote a healthier nursing experience for both mother and baby. Speech Difficulties: Restricted tongue mobility associated with tongue tie can contribute to speech difficulties in both children and adults. The impaired movement, shape, and placement of the tongue affect articulation and speech clarity. Many individuals with a tongue tie require speech therapy, yet struggle to overcome their speech challenges fully. Early identification and intervention can help improve tongue function and enhance speech outcomes. Picky Eating: A tongue tie can influence eating patterns and contribute to picky eating behaviors. Limited tongue mobility may make it challenging for individuals to manipulate food in their mouths, affecting chewing and swallowing. Difficulties in moving the tongue to different areas of the mouth can lead to aversions to certain textures or difficulty managing different food consistencies. Treating tongue tie can positively impact oral function, promoting a more diverse and nutritious diet. Clenching and Grinding Teeth: Tongue tie-related muscle imbalances can lead to clenching and grinding of teeth, known as bruxism. The altered tongue posture and muscle dynamics result in excessive muscle tension, causing teeth grinding during sleep or periods of stress. When the tongue is restricted and not able to rest fully against the palate, it may fall back into the airway during sleep which can lead to grinding as the body's way to try an open the airway. Treating tongue tie and addressing associated muscle imbalances may help reduce bruxism and alleviate related symptoms. Poor Sleep: A tongue tie can interfere with proper breathing patterns during sleep, contributing to sleep-disordered breathing conditions such as snoring, sleep apnea, and mouth breathing. These disturbances affect the quality and restfulness of sleep, leading to daytime fatigue, irritability, and poor concentration. Identifying and addressing tongue tie can improve airflow, promote nasal breathing, and support healthier sleep patterns. Mouth Breathing: The restriction caused by tongue tie may lead to compensatory mouth breathing. Mouth breathing can have detrimental effects on oral health, facial development, and overall well-being. It can result in dry mouth, increased risk of dental decay, altered facial growth patterns, and reduced oxygenation. Treating tongue tie and promoting nasal breathing helps restore proper oral function and encourages healthier breathing habits. Digestive Issues: A tongue tie can impact digestion and gastrointestinal function. Inadequate tongue movement affects chewing efficiency and can impair the initiation of the swallowing process. This can contribute to digestive problems such as acid reflux, bloating, and difficulty with food passage through the digestive tract. Addressing tongue tie and improving oral function can positively impact digestive health. Headaches and Neck and Shoulder Tension: The altered muscle dynamics and compensatory muscle patterns resulting from tongue tie can cause chronic headaches and increased tension in the neck and shoulder muscles. The strain on the muscles supporting the head, neck, and shoulders can lead to recurring headaches and muscular discomfort. The constant muscle tension may trigger tension headaches or migraines and contribute to neck and shoulder pain. By releasing a tongue tie, combined with myofunctional therapy, which focuses on restoring proper tongue posture and promoting balanced muscle activity, individuals may experience relief from headaches and reduced muscle tension. Jaw Pain: A tongue tie can contribute to jaw pain and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. The restricted tongue posture and altered muscle dynamics can affect the alignment and function of the jaw. Individuals with tongue tie may experience jaw pain, difficulty in opening or closing their mouths fully, clicking or popping sounds in the jaw joint, and even lockjaw. Treating a tongue tie and addressing associated muscular imbalances can help alleviate jaw pain and promote proper jaw function. Poor Posture: A tongue tie can impact overall posture. The tongue plays a crucial role in maintaining proper head and neck posture, as it helps support the alignment of the craniofacial structures. When tongue mobility is compromised, individuals may exhibit forward head posture, rounded shoulders, and an altered alignment of the spine. Addressing a tongue tie can contribute to improved posture and overall musculoskeletal health. Chronic Ear Infections: A tongue tie can be associated with an increased risk of chronic ear infections, particularly in children. The restricted tongue movement and altered muscle function can affect the Eustachian tube's ability to drain fluid from the middle ear properly. This can result in a buildup of fluid, leading to recurrent infections and potential hearing problems. Identifying and treating tongue tie can help address the underlying cause of chronic ear infections and reduce their occurrence. Crowded Teeth: A tongue tie can contribute to dental crowding and malocclusion. During the growth and developmental years, proper tongue posture against the palate is crucial in stimulating the jaws to grow wider and forward. This means more room for the adult teeth to fit and more airway space. The tongue also exerts natural pressure on the teeth during swallowing and rest, helping to guide their proper alignment. However, when tongue mobility is restricted, this pressure is diminished, and the teeth may shift and become crowded. Treating a tongue tie and improving oral function through myofunctional therapy can aid in maintaining proper dental alignment and reducing the need for orthodontic interventions. Conclusion: A tongue tie, though often overlooked, can have a significant impact on various aspects of an individual's health and well-being. From difficulties in nursing as infants to speech challenges, sleep disruptions, and associated issues throughout life, the consequences of untreated tongue tie can be far-reaching. Fortunately, myofunctional therapy provides a comprehensive approach to assessing and treating tongue tie, focusing on improving oral function, promoting proper muscle balance, and addressing the associated complications. If you or a loved one suspect the presence of a tongue tie or experience any of the related symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional experienced in orofacial myology for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan. By addressing the impact of tongue tie and its associated complications, we can unlock a healthier, and happier life for individuals of all ages. Did you know that the resting position of your tongue has a significant impact on your health and appearance? Proper oral rest posture, where the tongue rests against the roof of the mouth with lips sealed and teeth slightly apart, promotes healthy nasal breathing, supports facial muscle harmony, and influences the development of jaws and teeth.
During childhood, maintaining correct tongue posture helps drive forward growth of the upper jaw, resulting in a wider dental arch, higher cheekbones, and a more defined jawline. However, factors like mouth breathing, tongue ties, and sucking habits can lead to incorrect tongue posture. Seeking guidance from a Myofunctional Therapist can help address these issues and restore proper tongue posture, supporting overall well-being. Remember to keep your tongue up, lips closed, and breathe through your nose for optimal health. Be well! |
AuthorAuthor: Andrea Melnyk, RDH, BSc, COM Archives |






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed